Septic Tank Armadale gathers wastewater from the toilet, washing machine, garbage disposal, and other drains in your home. Bacteria digest and break down solid waste, with heavy solids settling to the bottom of the tank and oils and grease floating to the top.
A baffle or sanitary tee sits at the inlet and outlet to direct and control wastewater flow. It also keeps floating solids from entering the tank outlet pipe.
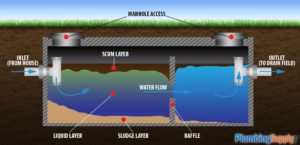
Every time you flush a toilet or wash your clothes, wastewater passes from your home through pipes into the septic tank. Here it’s treated by natural and mechanical processes. Heavy solids drop to the bottom of the tank forming a layer of sludge, while light solids and fats float to the top of the liquid. Bacteria and enzymes break down the sludge. Liquid wastewater (effluent) then leaves the septic tank through a pipe into the drain field.
Once outside, gravity forces the effluent through perforated pipes that filter it through rocks, dirt, and sand to remove disease-causing organisms and organic matter. It then seeps into the soil where natural processes further treat it to become clean groundwater.
Most septic tanks are made of concrete, fiberglass or polyethylene. Steel tanks rust and have shorter lifespans than other materials, but they’re still found in older systems. Newer tanks are usually built from sturdier fiberglass or polyethylene.
The tank consists of two chambers separated by a wall with openings near the middle. Sewage and wastewater enter the first chamber, where it’s held until solid waste separates from the liquid. The sludge layer falls to the bottom of the tank, while FOG floats to the top as a scum layer. Over time, anaerobic decomposition reduces the volume of these layers, which need to be pumped out periodically.
A baffle in the inlet prevents sludge from entering the inlet pipe and clogging the tank, while a T-shaped outlet baffle stops scum and sludge from exiting the tank and traveling into the drainfield. This protects the microbes that are treating the wastewater.
Aerobic septic tanks use an oxygen pump to blow air into the tank’s liquid waste, which stimulates aerobic bacteria that are better at breaking down sewage than other types of microbes. These bacteria are more efficient and require less space than the anaerobic microbes in traditional septic tanks, which reduces the size of the drain field needed to process wastewater. An alarm is triggered if the air pump fails. The wastewater then flows into a distribution box, which channels the fluid through perforated pipes set in trenches filled with stone or gravel.
Septic tanks are a necessity for those who live in rural areas without access to city sewers. They provide onsite water treatment and are environmentally friendly. They can also save you money by eliminating costly plumbing repairs and sewer services. Before installing a septic system, you should consult with local plumbing experts about your property and needs. They will give you recommendations about the type and size of septic tank that will work best for your home. They will also recommend a reliable septic tank installer for the job.
A septic tank is a large, buried, and watertight container that holds the wastewater from all the pipes in your house. Its size depends on the number of people living in your home and the amount of water use. A septic tank that is too small will quickly overflow with waste and cause severe problems.
The septic tank works by separating the solids from the liquids. The heavier solids, known as sludge, settle at the bottom of the tank while the lighter grease, oils, and lipids float on top. Inside the tank, colonies of bacteria break down these substances. The liquids, called effluent, then flow out of the septic tank and into the drain field.
Once the sewage leaves the septic tank, it seeps into the soil via perforated pipes. The effluent slowly filters into underground aquifers. It is important to plant grass and other shallow-rooted plants over the absorption area. This helps prevent the growth of roots that can penetrate and clog the septic system.
Before the septic tank installation, the plumbing expert will inspect your land and dig test pits to check the soil conditions. They will determine whether the soil is suitable for a septic system, checking factors like the soil types, the water table, and any buried structures that could interfere with drainage. They will also check for the presence of any tree roots that might penetrate the septic pipes and block them. Finally, they will conduct a land survey to ensure that the proposed site for the septic tank is actually within your property boundaries.
Septic tanks are designed to collect sewage and provide a quiet zone for the waste while colonies of bacteria break it down. The sludge and scum that accumulate in the tank decrease its working capacity over time, so it is important to keep the tank pumped out. It is also a good idea to perform regular system inspections and cleaning. This will help to prevent many problems, from costly repairs to clogged drain fields.
It is important to save all maintenance records on your septic tank, including inspections, cleaning and pumping. This information will come in handy if you ever decide to sell your home, as potential buyers will want to know that the septic system has been regularly maintained and cleaned.
A septic tank must be pumped every three to five years, depending on the number of people living in your household. The septic tank is a big part of the wastewater treatment process, and if it isn’t properly maintained, it can lead to sewage backups and untreated water being released into the environment. Backed up toilets and drains, as well as strong sewage odors, are signs that your septic system needs to be inspected and serviced.
During routine maintenance, your septic tank will be pumped and the contents examined for any signs of damage or leaks. It is also a good idea to map out the location of your septic tank and other system components, or to have them marked with stakes. This will prevent you from damaging the system when doing yard work or construction projects around your home.
It is also a good idea to avoid flushing anything that will not break down in your septic system. Items such as cigarette butts, paper towels, and diapers should be thrown in the trash instead of down the toilet. These items can clog the drains and increase scum formation in the tank. In addition, homeowners should avoid planting trees or any plants with deep roots over the drainfield. This will prevent the roots from growing into and clogging the pipes.
It is also a good idea to use the garbage disposal sparingly, as this can also increase the amount of solids in your tank. In addition, it is a good idea to have an effluent filter installed, as this can reduce the frequency of septic tank pumping.
When you have a septic tank, you need to know how much it costs to maintain it. Septic tanks are designed to treat sewage and wastewater, making them an efficient option for homeowners who live in rural areas. The cost of a septic system varies depending on the size and type of tank and the amount of waste it can handle.
The septic tank is the main component of a septic system and can range in price from $500 to $14,000 or more. The price of the septic tank depends on the material, size, and installation method. The cheapest tanks are made of fiberglass or polyethylene, while the most expensive ones are concrete.
Choosing the right septic tank for your home is crucial to reducing the overall cost of a septic system. The tank size ties directly to the number of bedrooms in your home, and the size of the septic system must match your household’s wastewater production. A three-bedroom home requires a larger tank than a two-bedroom home, and the tank must be deep enough to contain all the waste produced by the house.
A septic tank is usually buried underground, and the only access point is a manhole cover located on the ground surface. Having a septic tank riser installed can make it easier and less expensive for you to access your tank and prevent damage. Risers are available in both plastic and concrete and can be inserted into existing or new tanks.
When the septic tank is full, the heavier solids (sludge) settle to the bottom while the lighter liquids and gases move to the top. The septic tank’s baffles help to separate these layers, and the waste flows down into the drain or leach field. Here, the effluent is treated by microbes and soil to become clean wastewater.
Your septic system’s drain or leach field must be designed to carry the wastewater back into the soil. It should also be at least 50 feet away from any potable water wells. You can choose from several different types of septic systems, including mound systems, drip distribution systems, or engineered septic systems.